Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Treatment
Mike Hasn't Felt This Good In 35 Years Thanks To Dr. Williams
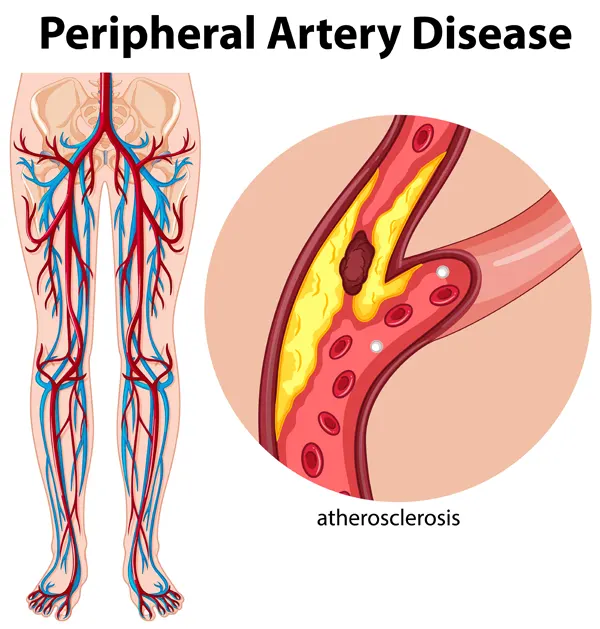
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
PAD Explained
Diagnosing PAD
Plaque, which consists of cholesterol and/or calcium can accumulate in the arteries supplying blood to your extremities, narrowing them, and lowering blood flow. The process by which plaque builds up within the walls of arteries and clogs them is called atherosclerosis, or “hardening of the arteries.”
One in every 20 Americans is plagued with PAD, which is a serious condition that needs to be diagnosed promptly by vascular specialists to decrease your long-term risk as much as possible.
What Are The Symptoms of PAD?
Patients with PAD are at increased danger of a heart attack or stroke and some may be at risk of losing a limb as the result of non-treatment. If detected early, arterial disease may be treated conservatively using a healthy lifestyle, diet, activity, and medicine. However, if left unchecked, the condition might develop to the point where it causes discomfort. Symptoms can include:
- Leg pain, heaviness, or numbness when climbing stairs or walking.
- When you are resting or sleeping, a burning pain in your toes and feet that is excruciating.
- Wounds or sores on your legs, feet, and toenails that do not heal.
- Your feet might become pale or blue because of the decreased blood flow.
- Decreased hair growth on legs and toes or poor nail development
- Erectile dysfunction, especially if you have diabetes, is a frequent problem among males.
More intensive therapy, in more severe instances of PAD, may be required to keep the condition from progressing further.
What type of treatment is available for peripheral artery disease (PAD)?
PAD Treatment Options
Minimally Invasive Techniques
At MIVA, we utilize a variety of sophisticated minimally invasive arterial procedures to treat complicated cases of PAD. Depending on the situation and its severity, it may include one or more of the following:
- Balloon Angioplasty
- Atherectomy
- Stent Placement
These are usually completed as outpatient procedures in our clinic, under moderate sedation. Depending on the unique needs and complexity of the case, the treatments might take one to four hours.
Why should you get in touch with MIVA Medical?
For leg discomfort, calf pain, or leg cramps at night, look no farther. MIVA Medical offers superior PAD treatment, providing a wide range of PAD therapy choices. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition in which arteries in the legs and feet become clogged. MIVA Medical offers innovative treatments for PAD.
What is an arteriogram with intervention, and how does it work?
“Arterio” means artery, and “Gram” is a word that means picture. We access your arteries using a tiny needle and thread a wire through the needle to access your arterial system. Using ultrasound and Xray guidance we make maps of your arteries using a dye that is injected into them. We can see where blockages are affecting the blood flow and identify where to target the treatment.
From here, we may do a variety of procedures:
- Balloon Angioplasty: This is a type of procedure in which a balloon is used to open an artery that has become narrowed or blocked. A special catheter with an elongated balloon on its tip is inflated to help open the artery and increase blood flow.
- Atherectomy is a non-surgical technique that removes plaque buildup in the arteries. This is done with a high-tech laser or grinding catheter to help break up plaque and restore blood flow.
- Stent Placement: A stent is a tiny cage inserted to keep an artery open if angioplasty or atherectomy does not restore blood flow as a last resort. This is a long-lasting implant.
Moderate sedation is administered at our facility, with a quick recovery time. A closure device is used to seal your artery, which reduces recovery time and may cause bruising or discomfort at the access spot.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do These Types Of Treatment Affect Blood Clots and Blood Flow?
Is MIVA the right place for PAD treatment?
The decision regarding whether to treat your arterial disease depends on your physician’s advice and a thorough physical examination by MIVA’s physicians. We might employ non-invasive imaging techniques such as ultrasound of the arteries, Pulse Volume Recording, or CT Angiography to diagnose your condition and recommend the most appropriate therapy.
Is it possible to get back up on my feet quickly?
Naturally, the length of time it takes to recover varies on the sort of therapy utilized. However, most patients report minimal recovery time. After undergoing treatment, we advise you to avoid heavy lifting for the first five days, but aside from this restriction, you are free to engage in your regular physical activity.
What is the best way to treat chronic leg pain?
Physical therapy may be the most recommended and best option for you if you have persistent leg discomfort and suffer from PAD symptoms . However, it is a promising idea to search for vascular causes of leg discomfort and cramps, such as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) or Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), in order to rule out other issues.
Additional Facts About Peripheral Artery Disease
Things You Need to Know About PAD in Missouri: Peripheral Arterial Disease Specialists
We understand that our reputation as the top peripheral vascular disease experts in Missouri entails a duty to educate the public about health issues that many individuals are unaware of.
How Do These Types Of Treatment Affect Blood Clots and Blood Flow?
These minimally invasive procedures that treat peripheral artery disease can help to increase blood flow in the blood vessels by widening narrowed or blocked arteries and helping improve high blood pressure issues caused by coronary artery disease and heart disease. But what can be done to prevent blood clots while still improving the target blood vessel or blocked artery? While angioplasty can improve the flow of blood, it can also increase the risk factors that can cause a blood clot. Fortunately, physicians can use a number of post-procedure techniques to minimize this risk, including anti-coagulation and anti-platelet therapies. With the proper care, angioplasty can be an effective tool for improving cardiovascular health.
Most people are unaware of the fact that peripheral arterial disease is far more common than many believe.
PAD affects at least 8 to 12 million people in the United States, according to some estimates. Over 200 million individuals worldwide suffer from PAD, six times higher than HIV for example.
The arteries in your legs are frequently the first indicators of a more significant medical condition.
Because many patients mistake tiredness and leg cramps as “natural indicators of aging,” the disease is often underreported. At the same time, physicians who fail to investigate it, even in individuals with other circulatory or heart issues, frequently misdiagnose it.
PAD, like other cardiovascular diseases, progresses slowly at first and is only detected when it has evolved into life-threatening limb ischemia and clogged arteries. As a result, over the past decade, there has been a shocking 23% increase in PAD cases worldwide.
What exactly is PAD, and how does it work?
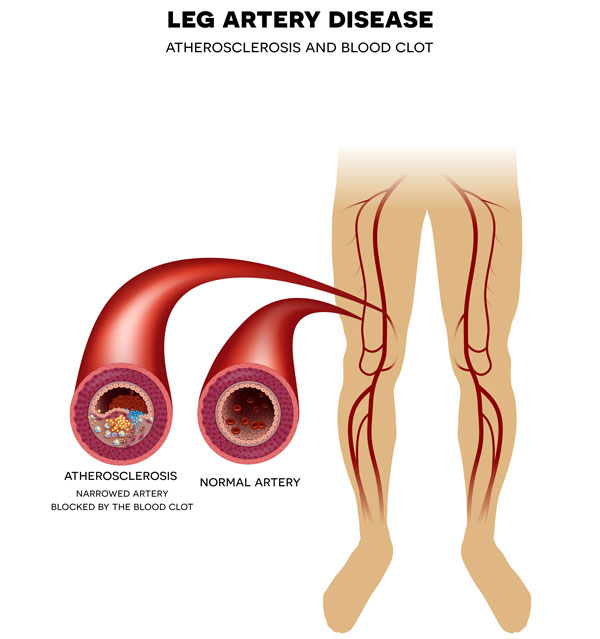
When fatty deposits clog your arteries, peripheral arterial disease occurs (plaque buildup). Cholesterol and other fats circulating in the body accumulate in the arteries supplying blood to your extremities.
Plaque builds up on the arterial walls, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. Atherosclerosis is the medical term for this process, in which plaque collects and hardens on the artery walls. When plaque accumulates it might form a blood clot that narrows or entirely blocks the artery.
Factors that put you at risk of getting PAD – the sources for developing PAD
- PAD is most common among those over 50.
- If you have ever smoked or if you currently smoke, you have a four times higher chance of getting PAD. This is the most significant risk factor for PAD.
- High blood pressure is linked to the development of plaque, which is a major cause of PAD.
- High blood cholesterol promotes plaque formation.
- 1 in 3 diabetics are likely to acquire PAD.
- Having a personal history of heart attack, stroke, or other vascular disease raises your risk of PAD to 1 in 3.
- PAD is hereditary, meaning that if one or more of your parents had it, you have a greater than 50 percent chance of getting it as well. If numerous family members have previously suffered from PAD, your chances of developing it are almost twice those of someone who does not have such a history. The danger is even higher if their PAD surfaced before the age of 68.
- Men and women are equally affected by PAD, but African Americans are more than twice as likely to get it when compared to other ethnicities.
There are numerous hazards of PAD developing.
PAD can have a huge influence on your life, from limiting your mobility to increasing your risk of heart attack and stroke. Untreated PAD can cause difficulty walking and has been linked to decreased life expectancy. PAD also raises the chance of a heart attack, stroke, or TIA (transient ischemic attack). Recent studies have shown that:
- Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is characterized by moderate to severe narrowing of the arteries in your legs and arms. The incidence of heart disease and cerebrovascular disease among patients with PAD can increase from 30%-60%.
- In 5 years, 10%–15% of PAD patients with intermittent claudication (cramping leg pain) may die from heart conditions.
- Patients with PAD had a higher mortality rate than those who had suffered a heart attack and were comparable to people who had suffered a stroke in terms of death rates per year. PAD patients who also had diabetes were more likely to die and experience other serious medical problems.
Finally, PAD can impair circulation to your extremities to the point that it leads to gangrene and/or limb or foot amputation in its most severe forms. PAD is the leading cause of lower limb amputation.
Take Our Quiz To Learn More